To simply put, data driven decision making means the use of facts, figures, records and past evidence to guide business decisions rather than depend on guesswork,instinct, or assumptions. It is like having a chart, compass or map to direct your journey instead of travellingpurposelessly and hoping to arrive at a destination. In today’s world, where information technology and business competitiveness are growing fast, companies that use data effectuallyare deemed to be well positioned to have a better chance of succeeding. Every business generates data whether it is sales figures, customer feedback, customer footprint, website visited, and product performance etc.
Example of data generated in businesses:
- A shop owner can track which products sell best at certain times of the year.
- A bank can study customer spending habits to offer tailored services.
- An online business can analyze how many people visited their website and which products they browse most.
- Business can segment customer based on their spending habits or product procured.
- Telecom companies can monitor when data traffic are highest etc.
Being data driven, means gathering these information, study them, analyse them, and using them to make well informed decisions. Instead of relying on guess work to take decisions, data driven decision are based on evidence and patterns revealed by data set collected overtime.
The Importance of Data for Businesses
1. Better/Informed Decisions Making: Imagine a business launching a new product, despite the level of feasibility studies carried out, it still tends to be trial and error because there is no existing data to work with, so this might not speak to a quantifiable degree the type products customers would actually want. By analysing sales trends and customer feedback overtime, they can launch products that meets real customers demand.
2. Saving Time and Money: Data helps businesses to identify what works and what does not. For example, if an advertisement is not generating sales, businesses can stop wasting money on it and focus on better or alternative strategies.
3. Improving Customer Experience: Data can conspicuously shows what customers cherished or not. A restaurant, for example, can analyse from sales overtime which dishes are most ordered and then make decision to increase and remove unpopular dishes to restructure operations to enhance customer satisfaction based on orders from data generated from past sales.
4. Staying Competitive: Businesses that use data can adapt quickly to market changes. If competitors are attracting customers with lower prices, data will show trends, and the business can adjust strategies to compete effectively.
Table 1.0below highlights the quantifiable benefits of data driven decisions across various industries, establishing how businesses can achieve tangible outcomes by analysing and acting on available data.
Table 1.0: Data driven decision and Outcome
| S/n | Business Type | Data Driven Decision | Outcome |
| 1 | Retail Store | Analyses customer purchase data to identify best-selling products. | Increased sales by 15% by stocking popular items early and reducing unsold inventory. |
| 2 | E-commerce Platform | Uses website traffic data to track which products are viewed and abandoned most. | Improved product promotions, leading to a 10% boost in conversions and sales. |
| 3 | Restaurant Chain | Tracks customer orders and reviews to identify top-performing dishes. | Reduced food wastage by 20% and increased customer satisfaction scores by 25%. |
| 4 | Telecommunications Customer Service | Analyzes call data, complaints, and service issues to predict customer dissatisfaction. | Proactively resolved issues, reducing customer complaints by 30% and churn rate by 12%. |
| 5 | Banking Institution | Uses transaction data to understand spending habits and target specific customer needs. | Increased uptake of savings products by 18% through personalised financial offerings. |
| 6 | Logistics Company | Uses delivery route and performance data to optimize delivery times and fuel usage. | Reduced delivery costs by 15% and improved on-time delivery rates to 95%. |
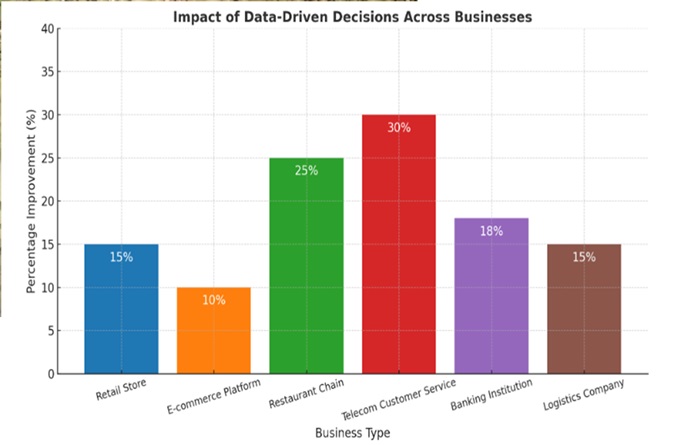
To compare these improvements to initial performance, the baseline data or the starting performance metrics of each business before implementing data driven decisions is as shown in below Table 2.0 including the ensuing improved performance and the % improvement.
Table 2.0: Hypothetical Baseline Performance and % Improvement
| S/n | Business Type | Baseline Performance | Improved Performance | Improvement (%) |
| 1 | Retail Store | N500,000 (sales) | N575,000 (sales) | 15% |
| 2 | E-commerce Platform | 5% conversion rate | 5.5% conversion rate | 10% |
| 3 | Restaurant Chain | 60% customer satisfaction | 75% satisfaction | 25% |
| 4 | Telecom Customer Service | 1000 complaints/month | 700 complaints/month | 30% |
| 5 | Banking Institution | 20,000 savings accounts | 23,600 savings accounts | 18% |
| 6 | Logistics Company | N50,000 (delivery cost) | N42,500 (delivery cost) | 15% |
The bar graph showing the percentage improvements achieved by different businesses through data-driven decisions. Each bar represents the measurable impact, such as increased sales, reduced churn, or improved efficiency, emphasizing the value of leveraging data in decision-making.
How Can Businesses Build a Data Driven Culture?
- Start Small:Businesses don’t need fancy tools to start. Basic steps like tracking sales, customer complaints, and inventory levels can already reveal important patterns.
- Invest in Tools and Skills:Businesses can use tools like Excel, Google Analytics, or more advanced systems to collect and analyze data. Employees need to be trained to use these tools effectively.
- Ask the Right Questions:To make decisions, businesses need to know what they are looking for.
For example:
- How can we attract more customers?
- Which product or service makes us the most money?
- What are the busiest hours of operation?
- Encourage Team Collaboration:Data is not just for managers. Sales, marketing, finance, and customer service teams should share and discuss insights to find the best solutions.
Challenges in Using Data
- Too Much Data:Businesses sometimes collect too much data without knowing how to use it. The key is to focus on the most important information that helps solve problems or improve processes.
- Resistance to Change:Employees used to traditional methods might resist relying on data. Businesses need to show how data makes their work easier and more effective.
- Data Quality:Decisions are only as good as the data. Businesses must ensure their data is accurate, up-to-date, and well-organized.
VI. A Real-Life Example
Imagine a retail store that tracks its sales data. After analyzing the numbers, they realize that most customers buy winter clothes in September, not December. This insight allows the store to stock up early, run promotions, and increase profits.
Another example is online platforms like Netflix, which use data to suggest movies based on what you have watched before. This keeps customers happy and engaged.
In conclusion, data driven decision making is the key to modern business success. It allows businesses to make smarter, faster, and more informed choices, leading to better results. Whether it is a small business or a large corporation, leveraging data helps improve efficiency, understand customers, and stay ahead of the competition. Businesses that embrace a data driven culture today will be the ones thriving tomorrow.
In our next column, we will be looking at Smart Cities: The Role of IoT in Creating Sustainable Urban Futures and Enhancing Our Business premises.
– Aji, Jacob Onu is currently a Ph.D. scholar in Information and Telecommunications Engineering and holds MSc. in information and telecommunications Engineering, an MBA, First Degree in Physics/Electronics. He has over 15 years expertise in information technology, business strategy, facilities management, Data Science and FMMC Ambassador. He writes about the intersection of technology, business, and innovation.




