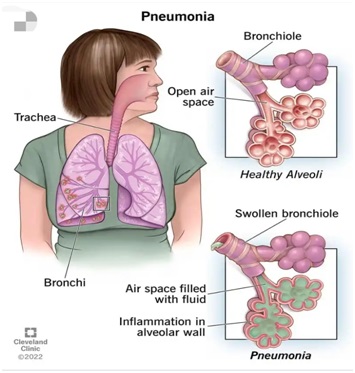
In Nigerian society, pneumonia is believed to be caused by being exposed to extreme cold weather conditions. This is not actually true as pneumonia is an infection of one or both of the lungs caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Pneumonia can develop when your immune system attacks an infection in the small sacs of your lung (alveoli). This causes your lungs to swell and leak fluids. Pneumonia is more prevalent in cold seasons not because it is cold but because people tend to be indoors more and in close contact. Pneumonia can develop as a secondary bacteria infection after a cold.
There are various types of pneumonia and the main types are:
Bacterial pneumonia: This type is caused by various bacteria. This often occurs when the body is weakened in some way such as, illness, poor nutrition, old age, or impaired immunity and the bacteria are able to spread into the lungs. Bacterial pneumonia easily affects people who abuse alcohol, smoke cigarettes, are debilitated, have recently had surgery, have a respiratory disease or viral infection, or have a weakened immune system.
Viral pneumonia. This type of pneumonia is caused by various viruses, including the flu (influenza), and is responsible for about one-third of all pneumonia cases. People with bacterial pneumonia are more likely to get viral pneumonia.
Mycoplasma pneumonia. This pneumonia has somewhat different symptoms and physical signs. It is referred to as atypical pneumonia. This is caused by the bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae. It generally causes a mild, widespread pneumonia that affects all age groups. There are other common pneumonias that may be caused by other infections including fungi.
Anyone can get pneumonia but people within the ages of 65 and older, children younger than two. People with certain medical conditions and smokers. The symptoms include, a persistent cough that may produce phlegm or pus pulse, difficulty breathing or rapid breathing, sharp or stabbing pain in the chest when breathing or coughing, bluish lips or nails, a sign of oxygen deprivation, fever, confused mental state or delirium, especially in older people, these among others are symptoms of pneumonia and it is advisable to to check into a hospital when any of these is experienced. It is crucial to note that symptoms may differ in children, the elderly, or individuals with underlying health conditions.
Possible Preventive Measures
Preventing pneumonia involves practicing good hygiene and taking certain precautions. Some preventive measures include:
Vaccination: Vaccines are available to protect against common causes of pneumonia, such as the pneumococcal and influenza vaccines.
Hand hygiene: Regularly washing hands or using hand sanitizers can help prevent the spread of respiratory infections.
Avoid Smoking: Smoking damages the lungs and weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, including pneumonia.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can help strengthen the immune system.
If you experience any of the symptoms, the first thing to do is to contact a healthcare provider who will conduct a thorough physical examination and possibly order additional tests such as a chest X-ray, blood work, or a sputum culture. These tests help identify the type of pneumonia and the most appropriate treatment.
Treatment
Treatment options for pneumonia depend on the cause and severity of the infection. Bacterial pneumonia is typically treated with antibiotics, while viral pneumonia generally requires rest, medications to alleviate symptoms, and time for the body to fight off the virus. Antifungal medications are prescribed for fungal pneumonia.
Conclusion
Remember, early intervention is key to a speedy recovery and the prevention of further health complications.
– Adeyi Confidence Ojonanyi
Mass Communication Student,
Prince Abubakar Audu University Anyigba, Kogi State.